#laravel fetching data from database
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
What Is PHP

What Is PHP, and why is It Still Essential in Web Development
PHP (short for Hypertext Preprocessor) is one of the most widely used scripting languages for building websites and web applications. It’s open-source, free to use, and runs on the server, meaning it processes tasks before content reaches your browser. Whether you're logging in to a website, filling out a form, or browsing dynamic content, chances are PHP is working behind the scenes.
In this post, we’ll break down what PHP is, what it’s used for, and why it continues to be a key part of modern web development.
What Is PHP?
PHP is a server-side scripting language that runs on web servers like Apache or Nginx. It helps developers build dynamic websites, meaning the content can change based on user input or data from a database.
Instead of just showing static pages, PHP allows for things like:
Displaying personalized user dashboards
Submitting and processing forms
Handling logins and registrations
Connecting to databases and fetching content
Key Features of PHP:
Server-Side Execution: Code runs on the server and sends the result to the browser.
Database Friendly: Easily connects with databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQLite.
Form Handling: Collects and processes data from HTML forms.
Session Management: Tracks users across pages (great for logins and shopping carts).
Platform Independent: Works on Windows, macOS, Linux—pretty much anywhere.
Large Community & Resources: Tons of tutorials, tools, and frameworks like Laravel.
What Is PHP Used For?
PHP is used for building all kinds of websites—from small personal blogs to full-scale eCommerce platforms. Let’s look at the common ways developers use PHP:
1. Dynamic Website Content
PHP helps create websites that change depending on who is visiting or what they’re doing. Think of personalized greetings, product recommendations, or updating shopping cart totals without refreshing the page.
2. Working With Databases
Need to store user data, products, or blog posts? PHP connects smoothly with databases like MySQL to save and fetch information, making it easy to manage large websites.
3. Handling Forms
When users fill out a form—say, to sign up or contact you—PHP processes that data. It checks if everything’s filled out correctly and then stores or emails the info.
4. User Sessions
PHP helps websites remember who you are as you move between pages. This is essential for things like staying logged in or remembering items in your cart.
5. Security and Automation
PHP allows you to add basic security layers, like input validation, data encryption, and access control. It’s also used for sending emails, generating PDF invoices, or even auto-posting to social media.
Is PHP Frontend or Backend?
PHP is strictly a backend language. While it works alongside frontend tools like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, PHP runs on the server. It handles all the logic behind the scenes—things like checking passwords, fetching data, or updating user info.
Why PHP Still Matters Today
Even with new languages and frameworks entering the scene, PHP remains highly relevant. It powers big names like Facebook (originally built on PHP), WordPress, and Wikipedia. Plus, frameworks like Laravel have modernized PHP, making development faster and cleaner.
In short, PHP is still a reliable, powerful choice—especially for developers building secure, data-driven websites.
Conclusion
PHP might not always be in the spotlight, but it's still the backbone of the web. It’s fast, flexible, and works well with almost anything. If you're planning to build a dynamic website or web application, learning PHP is a solid first step—and it’s not going anywhere anytime soon.
0 notes
Text
Build a Strong Backend: Why Web Developers Should Focus on MySQL Early

Introduction
When it comes to web development, most beginners are fascinated by the visual aspects of websites—the buttons, layouts, and animations. But behind every great website lies a powerful backend, and one of the most essential components of this backend is the database. Among the many database management systems out there, MySQL stands out as the most widely used and beginner-friendly option. If you're planning to enroll in a web development course in Yamuna Vihar or web development training in Uttam Nagar, it’s important to understand why you should prioritize learning MySQL early in your journey.
What is MySQL and Why is it So Important?
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system. It is used to store, organize, and retrieve data for web applications. It powers some of the world’s biggest platforms including Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube. For any student taking web designing classes in Yamuna Vihar or web development coaching in Uttam Nagar, learning MySQL is a non-negotiable step.
Why? Because it’s the heart of how web apps interact with data. Whether it’s a login system, product catalog, or a content management system—MySQL is what makes these features function.
Early MySQL Skills = Long-Term Benefits
Students who start learning MySQL early gain a significant advantage:
Better understanding of backend logic
You’ll start understanding how data flows between the front-end and backend, giving you a complete picture of web development.
Stronger foundation for full-stack development
If you're aiming to become a full-stack developer, learning MySQL early prepares you for advanced backend frameworks like Node.js, Django, or Laravel.
Boost your job-readiness
Recruiters and companies look for developers who can handle the full development cycle—especially those with MySQL and database management experience.
If you’re taking a full stack web development course in Yamuna Vihar or searching for the best full stack developer course with placement in Uttam Nagar, you’ll notice MySQL is an integral part of the curriculum.
How MySQL Complements Front-End Skills
Even if your primary interest lies in UI/UX or front-end design, having a grip on MySQL sets you apart. For example:
UI elements like dropdowns or search bars often fetch real-time data from the backend via SQL queries.
Dynamic websites that display user data or product recommendations rely heavily on MySQL databases.
If you're already exploring UI UX free online courses with certificates in Yamuna Vihar or a user interface design course in Uttam Nagar, pairing that with MySQL will make your portfolio completer and more impressive.
Key Concepts You Should Learn in MySQL
Here are some essential MySQL concepts every web developer should master:
Database creation and table structures
SQL queries: SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
Joins and relationships
Data normalization
Indexing for performance optimization
These concepts are often covered thoroughly in a web development training institute in Yamuna Vihar or web development coaching center in Uttam Nagar.
Real-World Applications of MySQL
Whether you're developing an e-commerce website, a social media platform, or a blog, MySQL will help you:
Store user credentials securely
Handle product inventories
Maintain order history
Run analytics on user behavior
Students attending web designing coaching in Yamuna Vihar or web development classes in Uttam Nagar often work on real-time projects that require database connectivity, making MySQL a practical tool rather than just theoretical knowledge.
Conclusion: Start with MySQL to Stay Ahead
Web development is not just about what users see—it's also about how websites work behind the scenes. MySQL teaches you the logic and structure that bring data-driven websites to life. So, if you’re currently enrolled in or planning to join a web designing course in Yamuna Vihar or a web development course in Uttam Nagar, make sure MySQL is at the top of your learning list.
Whether your goal is to become a full stack developer, build your own website, or master UI/UX design, understanding databases like MySQL will take your skills to the next level.
Suggested Links:
Oracle Database Administration
MY SQL Training
PHP Development
#oracle database#MY SQL Training#PHP Development#Web Development course#Wed Designing course in yamuna vihar#Web designing course in uttam nagar
0 notes
Text
SysNotes devlog 1.5 (backend edition)
Hi all! In this post I will continue the development of my plurality management web-app SysNotes. Today I will be focusing mostly on setting up the databases for the app, as currently test data is stored in the code itself. This severely limits the interactivity and features of the web-app, so it is time to separate it.
In this devlog, I will explain the basics of databases and how the Laravel framework interacts with them to give you an idea of what goes on on my screen and in my brain while I code. This will just be an overview of some technical behind the scenes, nothing will have changed on the front end of the app.
If you missed the first devlog, you can find it here.
What is a database?
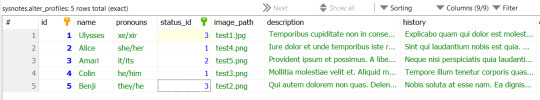
A database at the most basic level is a type of file format that has tables. You can think of it as a "spreadsheet file" like the ones you can open in Excel or Google Sheets. The main structural difference between a database and a spreadsheet is that in a database the tables can have relationships. For example, the relationship between a users table and a posts table is that one user can make many posts, and a post can only belong to one user. This is a one-to-many relationship. You can ask the database to give you all the posts related to a specific user. In my app, each user account will have multiple alter profiles, for example. When a user logs in, the app will only fetch the alter profiles that this user created, and show the profiles to them. You can do a whole bunch of other things with databases, that's why I like them! The main functional difference between a database and a spreadsheet is that a spreadsheet is used for data analysis and manipulation, like a fancy calculator, while a database is used to store data. Each table stores data related to one type of object/person/place. Like how spreadsheets can be opened in Excel, database tables can be opened in database software such as MySQL Workbench or HeidiSQL, which is what I'm using since it came with Laragon.
(What my Heidi DB looks like at the end of the devlog)

Plan for today
The users table already exists in my app as a result of installing the Laravel Breeze starter kit, so I don't have to worry about designing this table. With that out of the way, I can think about adding feature-related tables. The first feature I'm adding to my app is the ability to create alter profiles and to fill in the sections on the profile page. The first step is therefore to create an "alter profiles" table and to normalize it (more on that in a bit).
Setting up the database tables (and why it's a pain)
Migration files
When using the Laravel framework, you're not supposed to create a new table or edit an existing table through the database itself - it has to all be done through code. This is done using a file called a database migration. The migration specifies the table name, what columns it should have, what data types the columns should be, and what other tables this table may be related to. This is done so that if you give the code to another person and they download and ran it, their database will be set up the exact same way is yours. Therefore, the migration file makes your database changes portable, which is especially useful when copying code from your personal computer onto the server where the web-app is running. You don't want to set up your local database and then find out that it doesn't work the same way as the one that runs the actual app! Migrations aren't just for creating a new table. You also need to make a migration file for every structural change you want to make for that table, such as adding a new column or changing a column's name. Updating a table's structure after it's already been set up and filled with data has a chance of corrupting the data. Therefore, I always impose this expectation of myself of always getting the database structure right on the first try (i.e. in just one migration).
(My migration file for the alter profiles table at the end of this devlog)

Normalization
Normalization is the act of splitting up a table into 2 or more tables in order to simplify the data structure, reduce duplication, and make database queries more efficient. To illustrate, let's consider the alter profiles table. An alter can have several traits, such as "energetic" or "nervous" and so on. Let's say we should store it in a "traits" column like so:
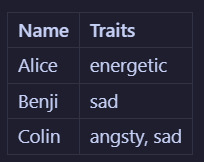
Now let's say we decide that the word "sad" isn't quite the right descriptor, and we want to change it to "melancholic". To do that, we would need to edit every instance of this word in the table. In this example, it would only be in 2 places: on Benji's profile and on Colin's profile. But what if there were many melancholic alters? That sounds like a lot of work! What if you misspell it on accident somewhere? You won't be able to filter alters by trait properly! Instead what would be better to do is to split (haha) the alter profile table into that and a traits table. Now we will have:
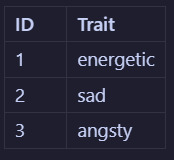
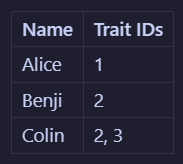
So if you wanted to change the word "sad" to "melancholic", you could do it in just one place, which makes it easier and more maintainable. This is just one small example of what normalization can be. There are actually like 7 levels of it, and even I don't remember them all. In fact, what I will be doing in my app is a step further than the example and use something called a "pivot table" - a whole new type of headache! The point is, figuring out the architecture of database tables is a whole science in on itself 😩
Actually doing the coding
After brainstorming how to normalize it, the alter profile will need to be separated into several tables: alter profiles, alter characteristic types (traits, likes, dislikes, an triggers), alter characteristic values, and alter statuses (such as active, dormant, and unknown). Each profile can then reference the characteristics and statuses tables. This way, alters can like or dislike the same thing, creating the ultimate modularity!

The (pretty technical) steps are as follows:
Create the (model with) migrations for the individual tables and specify their table structure
Create a pivot table and set foreign IDs to point to the individual tables
Define the relationships in the model files
It took me a few tries to get past migration errors, and I accidentally rolled back my migrations too many times, losing my users table 🤦♂️ As i don't yet have any alter data in the database, I just re-registered my account and nothing was lost. Heart attack simulator lol.
Seeding data
As I'm just working with test data, I don't really care exactly what words and images are used where as long as it works. I also don't want to pain-stakingly input test data into every field for every profile every time I have to delete (drop) and remake (migrate) a table. That's where seeding comes in. Seeding is an automated process that generates dummy data and inserts it into the database, ready for me to test. I'll admit I've never done seeding before - at work I've always worked with a copy of an existing database that has been filled by years of use. But it's never too late to learn! I used seeding to create dummy data for alter profiles and trait values (trait types and statuses has to be manually inputted because they have pre-defined values). I couldn't quite figure out how to seed pivot tables, as they define relationships rather than data. So I had to add those manually too. I still have a ways to go until I'm a real developer lol.
(My Alter Profile factory at the end of the devlog - i left pronouns blank because I wanted them to somewhat match the names, so I added them manually afterwards)

(My Alter Profile seeder at the end of the devlog)
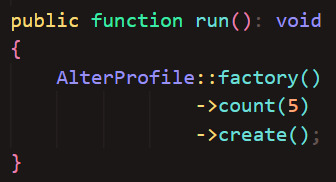
And here are my seeded tables! The faker is limited to using Latin words so I couldn't get the characteristics to look realistic. But it will be fine for test data.
(I have changed the alter names to match the names from the previous devlog)

...All this just for the profile page! But when designing a database's architecture, it is important to anticipate ways in which the database will grow and facilitate new relationships from the start. This was a tiring coding session but it has paved the way for the new and more exciting features!
What next?
This devlog was just for setting up the database tables - in the next devlog we'll get to actually use them in the app! The plan is:
Pull data from the database into the profile pages to display the freshly generated dummy data
Add a way to create new profiles using the New Profile form
Edit the profile information
0 notes
Text
Back-End Development: A Complete Guide for Beginners in 2025
When you visit a website, everything you see—the layout, colors, text, and buttons—is the front end. But what happens when you log in, fill out a form, or make a payment? That’s where the back-end development magic begins.
In this complete guide, we’ll explore what back-end development is, why it’s crucial for the web, what technologies and skills you need, and how you can build a thriving career in this dynamic field. Whether you're a curious beginner or someone switching careers, this article has everything you need to know.
🚀 What is Back-End Development?
Back-end development refers to the server-side part of web development. It's everything that happens behind the scenes to make a website or app function properly—like servers, databases, application logic, and APIs.
Back-end development is all about how a website works rather than how it looks.
For example:
When you submit a login form, the back end checks your credentials in the database.
When you place an order online, the back end processes the order and stores the transaction.
⚙️ How Does Back-End Development Work?
The back end interacts with three key components:
Server – The machine that handles requests.
Database – Where data like user info and product listings are stored.
Application – The logic that ties it all together.
Here’s a simplified flow:
User clicks a button (front-end)
Front-end sends a request to the server
Back-end processes the request
Data is fetched from or saved to the database
Server sends a response back to the front-end
🧰 Core Technologies in Back-End Development
To become a back-end developer, you’ll need to learn these foundational tools and languages:
1. Programming Languages
LanguageUse CaseJavaScript (Node.js)Scalable server-side appsPythonFast prototyping, AI, APIsPHPWordPress and server scriptingRubyElegant, readable server-side codeJavaEnterprise-grade backend systemsC# (.NET)Enterprise, Windows-based applications
2. Databases
TypeExamplesRelationalMySQL, PostgreSQL, MS SQL ServerNoSQLMongoDB, CouchDB, Firebase
3. Frameworks
LanguageFrameworksJavaScriptExpress.js, Nest.jsPythonDjango, FlaskPHPLaravelRubyRuby on Rails
🌐 Back-End vs Front-End Development
FeatureFront-EndBack-EndFocusUser interface (UI/UX)Server logic and databaseLanguagesHTML, CSS, JSJS (Node), Python, PHP, JavaRuns OnBrowserServerPrimary ConcernDesign, interactivityLogic, data management, securityPopular ToolsReact, Vue, BootstrapDjango, Express.js, PostgreSQL
🧑💻 Roles & Responsibilities of a Back-End Developer
What does a back-end developer do?
Build APIs and server-side logic
Design and maintain databases
Secure user data and handle authentication
Ensure scalability and performance
Collaborate with front-end developers and DevOps teams
🛡️ Back-End and Security
Security is a core responsibility in back-end development.
Key areas include:
Data encryption
Secure APIs
Password hashing (bcrypt, Argon2)
Input validation
Authorization & Authentication (OAuth, JWT, etc.)
🧱 APIs and RESTful Architecture
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are bridges between the front end and back end.
Back-end developers often design:
REST APIs using HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
GraphQL APIs for flexible data querying
WebSockets for real-time communication
🔗 Database Management and ORM
Databases are the heart of any application.
Back-end developers use SQL for structured queries and ORMs (Object Relational Mappers) like:
Sequelize (Node.js)
Prisma
SQLAlchemy (Python)
Eloquent (Laravel)
📦 Hosting and Deployment
Once the server code is ready, it needs to be hosted.
Popular options:
Cloud: AWS, Google Cloud, Azure
Containers: Docker, Kubernetes
Serverless: Vercel, Netlify, AWS Lambda
CI/CD pipelines like GitHub Actions, Jenkins, and GitLab CI automate deployments.
🧠 Learning Path: How to Become a Back-End Developer
Here’s a structured roadmap:
Master a Programming Language – Start with Python or JavaScript (Node.js)
Understand the Internet and HTTP
Learn Databases – Start with MySQL or MongoDB
Build REST APIs
Practice Authentication & Security
Work with Real Projects
Use Git and GitHub
Explore DevOps Basics
Build a Portfolio with back-end apps
Contribute to Open Source
📊 Salary Insights and Job Opportunities (2025)
Back-end development is one of the most in-demand tech skills in 2025.CountryEntry-LevelMid-LevelSeniorIndia₹5–8 LPA₹10–20 LPA₹25+ LPAUSA$65K–$85K$90K–$120K$130K+UK£30K–£50K£55K–£75K£80K+
Common Job Titles:
Back-End Developer
Full-Stack Developer
API Engineer
Server-Side Developer
Cloud Functions Developer
💬 Real Developer Reviews
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “As a back-end developer, I love building things people don’t even realize they’re using. It’s like being a wizard behind the curtain.” — Neha R., Software Engineer
⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ “Python and Django made it easy to get started. The logic is so clean and powerful.” — Mike T., Backend Developer
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ “Every startup needs someone who can build scalable back ends. It’s a career with massive growth potential.” — Ritika D., API Architect
🧠 Best Learning Resources (Free & Paid)
Free Platforms:
freeCodeCamp
MDN Web Docs
The Odin Project
Paid Options:
Udemy
"Node.js: The Complete Guide"
"Python & Django Bootcamp"
Coursera
"Back-End Development by Meta"
edX
Scrimba
📌 FAQs About Back-End Development
Q1. Do I need a degree to become a back-end developer?
A: No. Many successful developers are self-taught. Bootcamps and real-world projects matter more than degrees.
Q2. Which is better: back-end or front-end?
A: It depends on your interests. If you enjoy logic, data, and server operations—back-end is for you.
Q3. Is Node.js good for back-end?
A: Yes. Node.js is fast, efficient, and widely used for scalable server-side applications.
Q4. How long does it take to become job-ready?
A: With consistent learning, you can become a back-end developer in 6–12 months.
Q5. What is full-stack development?
A: Full-stack developers handle both front-end and back-end tasks. They’re skilled in end-to-end development.
Q6. What are the best languages for back-end development?
A: Python, JavaScript (Node.js), PHP, Java, and C# are top choices in 2025.
✨ Final Thoughts: Is Back-End Development Right for You?
If you love building logic, handling real-world data, working with APIs, and ensuring applications run smoothly—back-end development might be your ideal career path.
It’s a high-demand, well-paying, and technically rewarding field with endless opportunities for growth, especially with cloud computing, AI, and big data booming.
Whether you dream of joining a tech giant or launching your own SaaS app, mastering back-end development opens the door to some of the most impactful tech roles of the future.
0 notes
Text
The Role of Telegram Bots in Modern Digital Ecosystems: A Technical Perspective
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital communication, Telegram bots have emerged as a powerful tool for automating tasks, enhancing user engagement, and integrating services. These bots, which are essentially software applications running on the Telegram platform, leverage the Telegram Bot API to interact with users and perform a wide range of functions. From customer support to content delivery, Telegram bots are reshaping how businesses and individuals interact with technology.
The development of Telegram bots is deeply rooted in web development practices, requiring a solid understanding of APIs, server-side programming, and database management. The Telegram Bot API, which serves as the backbone of bot development, is a RESTful interface that allows developers to send and receive data in JSON format. This API supports a variety of methods, such as sending messages, managing user interactions, and even handling payments, making it a versatile tool for creating dynamic and interactive bots.
To build a Telegram bot, developers typically start by setting up a webhook—a mechanism that allows the bot to receive real-time updates from Telegram. Webhooks are configured using HTTPS endpoints, ensuring secure communication between the bot and Telegram’s servers. Once the webhook is in place, the bot can process incoming messages, execute commands, and send responses back to users. This process often involves the use of server-side programming languages like Python, Node.js, or PHP, along with frameworks such as Flask, Express.js, or Laravel to streamline development.
One of the most intriguing aspects of Telegram bot development is the integration of external APIs and services. For instance, a bot designed for weather updates might fetch data from a third-party weather API, process it, and deliver the information to the user in a concise format. Similarly, e-commerce bots can integrate with payment gateways like Stripe or PayPal to facilitate seamless transactions. This ability to connect with external systems makes Telegram bots a valuable asset in creating end-to-end solutions for various industries.
User experience (UX) plays a crucial role in the success of a Telegram bot. Developers must ensure that the bot’s interface is intuitive and easy to navigate. This often involves the use of inline keyboards, custom reply markup, and rich media such as images, videos, and documents. Additionally, developers can employ Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to enable more sophisticated interactions. Libraries like Dialogflow or Rasa can be integrated to allow the bot to understand and respond to user queries in a conversational manner.
Scalability and performance are also critical considerations in bot development. As the number of users grows, the bot must be able to handle increased traffic without compromising on response times. This is where cloud-based solutions like AWS, Google Cloud, or Heroku come into play. By deploying the bot on a scalable infrastructure, developers can ensure that it remains responsive and reliable, even under heavy load.
Security is another vital aspect that cannot be overlooked. Since bots often handle sensitive user data, developers must implement robust security measures. This includes using HTTPS for secure communication, encrypting sensitive data, and adhering to best practices for authentication and authorization. Regular security audits and updates are essential to protect the bot from potential vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, the development of Telegram bots is a multidisciplinary endeavor that combines web development, API integration, UX design, and security practices. As the digital ecosystem continues to evolve, Telegram bots are poised to play an increasingly important role in automating tasks, enhancing user experiences, and driving innovation. Whether you’re a developer looking to build your first bot or a business exploring new ways to engage with customers, the possibilities are virtually limitless.
Make order Tg Bot or Mobile app from us: @ChimeraFlowAssistantBot
Our portfolio: https://www.linkedin.com/company/chimeraflow
1 note
·
View note
Text
Build Portfolio Website in Laravel 11: Your Comprehensive Guide
Building a portfolio website is an essential step for showcasing your skills, projects, and achievements in today's competitive world. Laravel 11, the latest version of the robust PHP framework, offers unparalleled tools and features to create a stunning and functional portfolio website. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the process of building a portfolio website in Laravel 11, ensuring you have a step-by-step roadmap to success.
Why Choose Laravel 11 for Your Portfolio Website?
1. Modern Features
Laravel 11 introduces enhanced routing, improved performance, and advanced tooling that make it the go-to choice for web development.
2. Scalability
Whether you're a freelancer or a business owner, Laravel 11's scalability ensures your website can grow as your portfolio expands.
3. Security
With built-in authentication and security features, Laravel 11 protects your data and provides peace of mind.
4. Community Support
Laravel’s vast community ensures you’ll find solutions to problems, tutorials, and plugins to enhance your website.
Key Features of a Portfolio Website
To build a portfolio website in Laravel 11, ensure it includes:
Homepage: A welcoming introduction.
About Section: Your background and expertise.
Projects: A gallery showcasing your work.
Contact Form: Easy communication.
Blog Section: Share insights and updates.
Responsive Design: Optimized for all devices.
Getting Started with Laravel 11
Step 1: Install Laravel 11
Start by setting up Laravel 11 on your local environment.
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel portfolio-website
Step 2: Configure Your Environment
Update your .env file to set up the database and other environment variables.
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=portfolio
DB_USERNAME=root
DB_PASSWORD=yourpassword
Step 3: Set Up Authentication
Laravel 11 offers seamless authentication features.
php artisan make:auth
This command generates routes, controllers, and views for user authentication.
Step 4: Design Your Database
Create tables for your portfolio items, such as projects, blogs, and user profiles. Use migrations to structure your database.
php artisan make:migration create_projects_table
In the migration file:
Schema::create('projects', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('title');
$table->text('description');
$table->string('image')->nullable();
$table->timestamps();
});
Run the migration:
php artisan migrate
Building the Frontend
Step 1: Choose a CSS Framework
Laravel integrates well with frameworks like Tailwind CSS and Bootstrap. Install Tailwind CSS for modern and responsive designs:
npm install -D tailwindcss
npx tailwindcss init
Configure your Tailwind file and integrate it into your project.
Step 2: Create Blade Templates
Laravel’s Blade templating engine simplifies building dynamic pages. Create a layout file in resources/views/layouts/app.blade.php:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>@yield('title')</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{{ asset('css/app.css') }}">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
@yield('content')
</div>
</body>
</html>
Use this layout in other views:
@extends('layouts.app')
@section('title', 'Home')
@section('content')
<h1>Welcome to My Portfolio</h1>
@endsection
Step 3: Dynamic Content
Fetch portfolio items from the database and display them dynamically using controllers.
public function index() {
$projects = Project::all();
return view('home', compact('projects'));
}
In your Blade template:
@foreach ($projects as $project)
<div class="project">
<h2>{{ $project->title }}</h2>
<p>{{ $project->description }}</p>
<img src="{{ $project->image }}" alt="{{ $project->title }}">
</div>
@endforeach
Advanced Features
1. Search Functionality
Add search to help visitors find specific projects or blogs.
public function search(Request $request) {
$query = $request->input('query');
$projects = Project::where('title', 'LIKE', "%{$query}%")->get();
return view('search-results', compact('projects'));
}
2. File Uploads
Enable uploading images for projects.
public function store(Request $request) {
$request->validate([
'title' => 'required',
'description' => 'required',
'image' => 'nullable|image',
]);
$imagePath = $request->file('image')->store('projects', 'public');
Project::create([
'title' => $request->title,
'description' => $request->description,
'image' => $imagePath,
]);
}
3. Integrate Analytics
Use Google Analytics or similar tools to track visitor behavior.
4. Deploying Your Website
Deploy your Laravel website using platforms like Laravel Forge, AWS, or Heroku. Ensure to optimize the performance with caching and minification.
Optimizing Your Portfolio Website for SEO
Keyword Integration: Use keywords like “Build Portfolio Website in Laravel 11” strategically in titles, meta descriptions, and content.
Fast Loading Times: Optimize images and use caching.
Responsive Design: Ensure compatibility with mobile devices.
Content Strategy: Regularly update your blog to attract organic traffic.
Conclusion
Building a portfolio website in Laravel 11 is an enriching experience that showcases your skills and work to the world. By leveraging the framework’s capabilities and integrating advanced features, you can create a website that stands out in the digital landscape. Start your journey today and make your mark with a professional portfolio website
0 notes
Text

Laravel Application Development - Sciflare Technologies Pvt. Ltd
Caching in Laravel plays a crucial role in optimizing application performance by reducing the time it takes to retrieve data and render views. It stores frequently accessed data in memory or storage (like Redis or Memcached), avoiding the need to regenerate or fetch data from the database repeatedly. This improves response times, decreases server load, and enhances overall user experience by delivering content more swiftly. Laravel provides convenient caching mechanisms through its caching API, enabling developers to implement caching at various levels such as routes, queries, and entire views, thereby optimizing application development and performance significantly.
#laravelapplicationdevelopment#laravelappdevelopment#laravemobileappdevelopment#laravelappdeveloper#laravelsoftwareprovider#laravelappdevelopmentcompany#laraveldevelopmentservices
0 notes
Text
Laravel Eloquent: Mastering the Art of Database Interactions
Laravel Eloquent is an Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) layer that comes built-in with the Laravel framework. It serves as an abstraction layer that allows developers to interact with databases using PHP objects and classes, rather than writing raw SQL queries. Eloquent simplifies the process of retrieving, inserting, updating, and deleting data from the database, making it more efficient and less error-prone.

One of the key features of Eloquent is its ability to represent database tables as models. Models are PHP classes that correspond to database tables, and each instance of a model represents a row in that table. Eloquent provides a set of methods and conventions that allow developers to define relationships between models, such as one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships.
Mastering the art of database interactions with Eloquent involves understanding the following concepts:
1. Model Definition: Creating models that correspond to database tables, defining table names, primary keys, and other properties.
2. Retrieving Data: Using Eloquent's query builder to fetch data from the database, including techniques like eager loading, chunking, and scoping.
3. Inserting and Updating Data: Creating new records, updating existing records, and handling mass assignment protection.
4. Relationships: Defining and working with one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships between models.
5. Eloquent Events: Handling events such as model creation, updating, and deleting, to perform additional logic or data manipulation.
6. Query Scopes: Defining reusable query constraints to simplify complex queries.
7. Accessors and Mutators: Customizing how Eloquent retrieves and stores data in the database, allowing for data transformation and formatting.
8. Eloquent Collections: Working with collections of models, and utilizing the collection's powerful methods for data manipulation and transformation.
9. Database Migrations: Using Laravel's migration system to create and manage database schema changes in a controlled and versioned manner.
10. Eloquent Serialization: Converting Eloquent models to and from various formats, such as JSON or arrays, for data transfer or storage.
By mastering these concepts, developers can leverage the power of Eloquent to build robust and scalable applications with efficient database interactions. Eloquent not only simplifies database operations but also promotes code organization, maintainability, and testability.
In Laravel, Eloquent models serve as the bridge between your application's logic and the underlying database. Each model corresponds to a specific database table, representing its structure and facilitating interactions with the records stored within that table.
Eloquent Model Structure
An Eloquent model is a PHP class that extends the base `Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model` class provided by Laravel. This base class provides a wide range of functionality for interacting with the database, including methods for creating, reading, updating, and deleting records.
Within an Eloquent model, you define the properties and relationships that correspond to the columns and associations of the respective database table. This includes specifying the table name, primary key, timestamps, and any additional attributes or behaviors specific to that model.
Defining Database Table Attributes
One of the primary responsibilities of an Eloquent model is to define the structure of the corresponding database table. This includes specifying the table name, primary key, and any other relevant attributes.
By default, Laravel follows a convention where the model name is singular, and the corresponding table name is the plural form of the model name. For example, a model named `User` would map to a table named `users`. However, you can override this convention by explicitly defining the table name within the model.
Models also define any timestamps columns (e.g., `created_at` and `updated_at`) and specify the primary key column if it differs from the default `id`.
Encapsulating Database Interactions
Eloquent models encapsulate all interactions with the database table they represent. This includes creating new records, retrieving existing records, updating records, and deleting records.
Instead of writing raw SQL queries, developers can leverage Eloquent's fluent interface, which provides a set of expressive methods for performing database operations. These methods allow you to build complex queries in a concise and readable manner, reducing the risk of SQL injection vulnerabilities and promoting code maintainability.
For example, to retrieve all records from a table, you can simply call the `all()` method on the corresponding model. To create a new record, you instantiate the model, set its properties, and call the `save()` method. Eloquent handles the underlying SQL statements and database interactions transparently.
Defining Model Relationships
Another crucial aspect of Eloquent models is the ability to define relationships between different database tables. Laravel supports various types of relationships, including one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many.
By defining these relationships within the models, you can easily access and manipulate related data without writing complex join queries. Eloquent provides methods for eager loading related data, reducing the need for multiple database queries and improving performance.
Overall, Eloquent models serve as the backbone of database interactions in Laravel applications. They encapsulate the structure and behavior of database tables, facilitate database operations through a fluent interface, and enable the definition of relationships between tables. By leveraging Eloquent models, developers can write more maintainable and expressive code while reducing the risk of SQL injection vulnerabilities and promoting code organization.
CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations are the fundamental actions that allow you to manage data in a database. Laravel's Eloquent ORM provides a set of methods that simplify these operations, making it easy to interact with database records without writing raw SQL queries.
Create
Eloquent provides several methods to create new records in the database. The most commonly used method is `create`, which accepts an array of key-value pairs representing the columns and their respective values. Eloquent handles the insertion of the new record into the database table.
Additionally, you can instantiate a new model instance, set its properties, and then call the `save` method to persist the record in the database.
Read
Retrieving data from the database is a common operation, and Eloquent offers a variety of methods to fetch records. The `all` method retrieves all records from the database table associated with the model. You can also use the `find` method to retrieve a single record by its primary key value.
Eloquent allows you to build complex queries using its fluent query builder, enabling you to filter, sort, and apply constraints to the retrieved data based on your application's requirements.
Update
Updating existing records in the database is straightforward with Eloquent. You can retrieve an existing record using methods like `find` or `findOrFail`, modify its properties, and then call the `save` method to persist the changes to the database.
Alternatively, you can use the `update` method to update one or more records in the database based on specific conditions. This method accepts an array of key-value pairs representing the columns and their new values, along with a condition specifying which records should be updated.
Delete
Deleting records from the database is handled by the `delete` method in Eloquent. You can retrieve a specific record using methods like `find` or `findOrFail` and then call the `delete` method on that instance to remove it from the database.
Eloquent also provides the `destroy` method, which allows you to delete one or more records based on their primary key values or specific conditions.
In addition to these fundamental CRUD operations, Eloquent offers several other methods and features that enhance database interactions. These include:
1. Relationships: Eloquent allows you to define and work with relationships between models, such as one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships, simplifying the retrieval and manipulation of related data.
2. Accessors and Mutators: These allow you to customize how Eloquent retrieves and stores data in the database, enabling data transformation and formatting.
3. Scopes: Scopes provide a way to define reusable query constraints, making it easier to build complex queries across your application.
4. Events: Eloquent provides a set of events that you can hook into, allowing you to perform additional logic or data manipulation before or after various database operations.
By leveraging Eloquent's methods and features for CRUD operations, developers can write more concise and expressive code while reducing the risk of SQL injection vulnerabilities and promoting code maintainability.
In relational databases, tables often have relationships with one another. For example, a blog post may have many comments, or a user may have multiple addresses. Laravel's Eloquent ORM provides a convenient way to define and work with these relationships between models, making it easier to retrieve and manipulate related data.
One-to-One Relationships
A one-to-one relationship is a type of relationship where one record in a table is associated with a single record in another table. For example, a `User` model might have a one-to-one relationship with an `Address` model, where each user has a single address associated with them.
In Eloquent, you can define a one-to-one relationship using methods like `hasOne` and `belongsTo`. These methods allow you to specify the related model and the foreign key column that links the two tables together.
One-to-Many Relationships
A one-to-many relationship is a type of relationship where a single record in one table can be associated with multiple records in another table. For example, a `User` model might have a one-to-many relationship with a `Post` model, where each user can have multiple blog posts.
Eloquent provides methods like `hasMany` and `belongsTo` to define one-to-many relationships. The `hasMany` method is used on the parent model (e.g., `User`), while the `belongsTo` method is used on the child model (e.g., `Post`).
Many-to-Many Relationships
A many-to-many relationship is a type of relationship where multiple records in one table can be associated with multiple records in another table. For example, a `User` model might have a many-to-many relationship with a `Role` model, where a user can have multiple roles, and a role can be assigned to multiple users.
In Eloquent, many-to-many relationships are defined using methods like `belongsToMany` on both models involved in the relationship. Additionally, you need to specify an intermediate table (often called a pivot table) that stores the mapping between the two models.
Defining Relationships
Relationships in Eloquent are typically defined within the model classes themselves. For example, in a `User` model, you might define a one-to-many relationship with the `Post` model like this:
```php
class User extends Model
{
public function posts()
{
return $this->hasMany(Post::class);
}
}
```
And in the `Post` model, you would define the inverse relationship:
```php
class Post extends Model
{
public function user()
{
return $this->belongsTo(User::class);
}
}
```
Working with Relationships
Once you have defined the relationships between your models, Eloquent provides several methods to interact with related data. For example, you can retrieve a user's posts like this:
```php
$user = User::findOrFail(1);
$posts = $user->posts;
```
You can also create new related records, update existing related records, and remove related records using Eloquent's relationship methods.
Eloquent relationships make it easier to work with related data in your application, reducing the need for complex join queries and promoting code organization and maintainability.
Query Scopes are a powerful feature in Eloquent that allow developers to encapsulate and reuse common query constraints or modifications. They provide a way to define reusable query logic that can be easily applied to Eloquent queries, enhancing code readability, maintainability, and reducing duplication.
What are Query Scopes?
Query Scopes are essentially methods defined within an Eloquent model that add additional constraints or modifications to the query builder instance. These methods can be chained together with other Eloquent query builder methods, allowing for the creation of complex and expressive queries.
There are two types of Query Scopes in Eloquent:
1. Local Scopes: These are scopes defined within a specific Eloquent model and can only be used with that model.
2. Global Scopes: These are scopes that are applied to all queries for a given model, regardless of where the query is constructed.
Benefits of Query Scopes
Query Scopes provide several benefits that enhance the development experience and code quality:
1. Reusability: By encapsulating common query logic into scopes, developers can easily reuse these scopes across different parts of their application, reducing code duplication.
2. Readability: Well-named scopes make queries more self-documenting and easier to understand, improving code readability and maintainability.
3. Testability: Since scopes are defined as methods within the Eloquent model, they can be easily unit tested, ensuring the correctness of the query logic.
4. Abstraction: Scopes abstract away complex query logic, allowing developers to focus on the higher-level application logic.
Using Query Scopes
To define a local scope, you create a method within your Eloquent model that returns an instance of the query builder with the desired constraints or modifications applied. For example, you might define a scope to retrieve only active users like this:
```php
class User extends Model
{
public function scopeActive($query)
{
return $query->where('active', true);
}
}
```
You can then use this scope when querying for users:
```php
$activeUsers = User::active()->get();
```
Global scopes, on the other hand, are defined using the `addGlobalScope` method within the `boot` method of your Eloquent model. These scopes are automatically applied to all queries for that model.
```php
class User extends Model
{
protected static function boot()
{
parent::boot();
static::addGlobalScope('active', function ($query) {
$query->where('active', true);
});
}
}
```
In addition to defining custom scopes, Eloquent also provides several built-in scopes, such as `whereKey`, `whereKeyNot`, and `latest`, among others.
By leveraging Query Scopes, developers can create more readable, maintainable, and testable code while reducing duplication and promoting code organization within their Laravel applications.
In Laravel, when you retrieve data from the database using Eloquent, the results are returned as instances of the `Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Collection` class. Eloquent Collections are powerful data structures that provide a rich set of methods for working with and manipulating the retrieved data.
What are Eloquent Collections?
Eloquent Collections are Laravel's implementation of the collection data structure, designed to store and manipulate collections of related objects or items, such as Eloquent models or arrays. They serve as a wrapper around the underlying data, providing a consistent and intuitive interface for interacting with that data.
Benefits of Eloquent Collections
Working with Eloquent Collections offers several advantages:
1. Fluent Interface: Collections provide a fluent interface with a wide range of methods for manipulating and transforming data, making it easy to chain multiple operations together.
2. Immutable Data: Collections are immutable, meaning that when you perform an operation on a collection, a new instance is returned, leaving the original collection unchanged. This helps prevent unintended side effects and promotes functional programming patterns.
3. Lazy Loading: Collections support lazy loading, which means that data transformations or operations are not applied until the collection is actually used or iterated over. This can lead to significant performance improvements, especially when working with large datasets.
4. Type Safety: Collections enforce type safety, ensuring that only objects of the same type are stored and manipulated within a given collection.
5. Consistency: Eloquent Collections provide a consistent interface for working with data, regardless of the source (e.g., database queries, arrays, or other collections).
Working with Eloquent Collections
Eloquent Collections offer a wide range of methods for manipulating and transforming data. Here are some common operations you can perform on collections:
Filtering: You can use methods like `filter`, `where`, `reject`, and `whereIn` to filter the items in a collection based on specific conditions or criteria.
Mapping and Transforming: Methods like `map`, `transform`, `flatMap`, and `flatten` allow you to apply transformations or operations to each item in the collection, returning a new collection with the transformed data.
Reducing and Aggregating: You can use methods like `reduce`, `sum`, `avg`, and `max` to perform aggregations or reductions on the data in the collection.
Sorting and Reordering: Collections provide methods like `sort`, `sortBy`, and `sortByDesc` for sorting and reordering the items based on specific criteria.
Retrieving and Checking: Methods like `first`, `last`, `contains`, and `isEmpty` allow you to retrieve specific items or check for the existence of items in the collection.
Eloquent Collections also integrate seamlessly with other Laravel features, such as pagination and caching, making it easier to work with large datasets and improve application performance.
By leveraging the power of Eloquent Collections, developers can write more expressive and maintainable code for manipulating and transforming data retrieved from the database, further enhancing the productivity and effectiveness of working with Laravel's Eloquent ORM.
Conclusion:
Laravel Eloquent empowers developers to master the art of database interactions by offering a clean, expressive syntax for working with databases. Its features, from simple CRUD operations to advanced relationships and query scopes, enable developers to build scalable and maintainable applications without sacrificing readability. Eloquent Collections, a powerful data structure, provide a rich set of methods for working with and manipulating retrieved data, making expertise in Collections highly valuable when looking to hire Laravel developers or partnering with a Laravel development company. By embracing Eloquent, Laravel developers can streamline their workflow, focus on creating innovative solutions, and make the database interaction process a joy rather than a challenge, ultimately delivering high-quality, efficient applications.
0 notes
Text
A Beginner's Guide to Database Interaction in Laravel Development
In the vast realm of web development, Laravel stands out as a robust and developer-friendly PHP framework. One of its key strengths lies in its eloquent ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) system, making database interaction seamless and efficient. In this beginner's guide, we will explore the fundamentals of database interaction in Laravel development, shedding light on the essential concepts that every aspiring Laravel developer should grasp.
Understanding Laravel's Eloquent ORM
Laravel's Eloquent ORM simplifies database operations by allowing developers to interact with databases using a more expressive and object-oriented syntax. Instead of writing raw SQL queries, developers can work with PHP models, making database interaction more intuitive.

Eloquent Models
In Laravel, an Eloquent model serves as a representative of a database table. By extending the Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model class, developers can create models that map directly to database tables. This abstraction allows for a cleaner separation of concerns, making it easier to manage and organize code.
For instance, if you have a users table in your database, you can create a corresponding User model in Laravel. This model not only represents the data structure but also inherits various Eloquent methods, enabling seamless interaction with the database.
CRUD Operations with Eloquent:
Eloquent simplifies CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations. Let's break down each operation:
Create (Insert):
To insert a new record into the database, you can create a new instance of the Eloquent model and set its attributes before calling the save() method. For example:
$user = new User;
$user->name = 'John Doe';
$user->email = '[email protected]';
$user->save();
Read (Select):
Eloquent provides various methods for retrieving data. The all() method fetches all records from a table, while find($id) retrieves a specific record by its primary key. Additionally, you can use the get() method with conditions using where():
$allUsers = User::all();
$userById = User::find(1);
$filteredUsers = User::where('status', 'active')->get();
Update:
Updating records is straightforward. Retrieve the record, modify its attributes, and call the save() method:
$user = User::find(1);
$user->name = 'Updated Name';
$user->save();
Delete:
Deleting records is as simple as calling the delete() method on an Eloquent model instance:
class User extends Model
{
public function posts()
{
return $this->hasMany(Post::class);
}
}
This allows you to retrieve a user's posts effortlessly:
$user = User::find(1);
$posts = $user->posts;
Query Scopes:
Eloquent allows you to define query scopes, which are reusable query snippets that can be applied to a model. This enhances code readability and encourages the use of consistent query logic.
class User extends Model
{
public function scopeActive($query)
{
return $query->where('status', 'active');
}
Now, you can use the scope like this:
$activeUsers = User::active()->get();
Connecting Laravel to a Database:
The first step in Laravel database interaction is establishing a connection. Laravel supports multiple databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, and SQL Server. Developers can configure the database connection settings in the config/database.php file, providing flexibility for different project requirements.
Fetching Data with Eloquent:
Eloquent provides a powerful and eloquent way (pun intended) to retrieve data from the database. Developers can use methods such as all(), find(), and where() to fetch records effortlessly. This not only enhances code readability but also promotes a more efficient development workflow.
Introduction to Laravel Query Builder:
For developers who prefer a more SQL-centric approach, Laravel offers the Query Builder. This feature allows the construction of SQL queries using a fluent interface, providing a balance between raw SQL and Eloquent ORM. It's a great choice for those who want more control over the query structure.
Leveraging Relationships in Eloquent:
One of the standout features of Eloquent is its ability to handle relationships between database tables. Whether it's a one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many relationship, Eloquent makes it easy to define and navigate these connections. Understanding relationships is crucial for designing efficient and scalable database structures.
Best Practices for Laravel Database Interaction:
To ensure optimal performance and maintainability, adhering to best practices is essential. This includes using eager loading to minimize the number of queries, implementing proper indexing, and handling database migrations carefully to keep the database schema in sync with the application.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, mastering database interaction is a fundamental aspect of Laravel development. Whether you're a newcomer to web development or transitioning from another framework, understanding Laravel's Eloquent ORM and Query Builder is key to building robust and scalable applications.
If you are looking for professional Laravel development services in the Netherlands, our team specializes in delivering top-notch Laravel web development services. Contact us to discuss how we can leverage Laravel's power to bring your web projects to life. Contact Us : https://maven-infotech.nl/ Call Us : NL: +31-(0)20 36 38 550
#laravel#laravel we devlopment service#laravel development company#laravel development services in netherland#laravel web development company in netherland
0 notes
Text
Laravel Performance Optimization: 5 Ways To Improve Page Load Times

The performance of your web application is the key determinant to make or break your success in the fast-paced digital landscape. Slow-loading web pages is a big red flag as it can frustrate and deter the user's attention span. If you want a higher SEO ranking and an enhanced user experience to hire dedicated Laravel developer can be the right decision.
Laravel’s performance optimization feature along with it’s other features can ensure speedy page load time. Let’s look at 5 effective ways to ensure Laravel performance optimization.
Why Hire Laravel Developer for Performance Optimization and Improved User Experience
Optimize Database Queries
Database queries often result in a low page load speed. To optimize these queries:
When you hire Laravel developer they use Laravel’s Eloquent ORM that has features like query optimization and eager loading to ensure reduced queries and efficient data retrieval.
Avoid the N+1 query problem where separate queries are made with the retrieval of a set of records. Eager loading can help retrieve related data in a single query.
Caching
This is a fundamental technique highly regarded to improve the page load time. Laravel has an intuitive and robust caching mechanism that stores frequently accessed data in a permanent storage solution like Redis. By using the built-in cache methods of Laravel such as `cache()`, `remember()`, and `forget()` you can reduce the time taken to retrieve and display information.
Asset Optimization
Large and unoptimized assets such as images, JavaScript, and CSS files slow down page loading. When you hire dedicated Laravel developer they use the following techniques to mitigate this issue:
Asset compression using tools such as Brotli or Gzip reduces the time taken by the browser to download them.
Minification of JavaScript and CSS files to reduce their size. Laravel Mix is a tool that can make the compilation and minification of assets easy.
Utilize Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for the global distribution of assets and ensure that users access resources from a server geographically close to them for enhanced load speed.
HTTP Caching
By reducing the need to fetch resources repeatedly, HTTP caching can further improve the page load speed. Laravel supports HTTP caching mechanisms such as ETag and Last-Modified headers that allow browsers to cache resources locally and request updates only when necessary. When you hire Laravel developers they employ this technique to reduce the load on your web server and minimize the transfer of redundant data for faster page loading.
Load Balancing and Scalability
As the web application evolves, it’s essential to address performance challenges through load balancing and scalability. The incoming requests are distributed across multiple web servers ensuring that a single server doesn’t become a bottleneck. Additionally, horizontal scaling helps attain scalability by adding more server instances for handling increased traffic.
Wrapping Up
As discussed above, page load times are crucial for rendering exceptional user experience and ensuring the competitiveness of the web application.
When you hire a dedicated Laravel developer you can significantly enhance the speed and efficiency of your web application with these techniques. Optimizing the performance of your application is essential for continued success.
0 notes
Text
The provided code appears to be a Laravel function for generating a PDF document using the mPDF library. This function takes a token as a parameter and fetches data from a database to create a PDF document. Here is the full function example:
This function retrieves the necessary data, configures mPDF, generates the PDF from a Blade view, and returns it as a response to the client. Please ensure you have the required dependencies and fonts set up for this code to work correctly in your Laravel project.

0 notes
Text
Fundamentals of PHP Application Architecture
Fundamentals of PHP Application Architecture
PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) has been a cornerstone of web development for decades, enabling developers to build dynamic and interactive web applications. To create robust, scalable, and maintainable PHP applications, it's essential to have a solid understanding of application architecture. In this blog post, we'll delve into the fundamentals of PHP application architecture, exploring key concepts and best practices.
1. Separation of Concerns (SoC):
One of the fundamental principles of PHP application architecture is the separation of concerns. This architectural pattern divides the application into distinct sections that handle specific responsibilities. In the context of PHP, this often translates into separating the presentation layer (HTML, CSS, and front-end interactions), the application logic (PHP code), and the data storage (database interactions). This separation enhances code readability, reusability, and maintainability.
2. Model-View-Controller (MVC):
MVC is a widely used architectural pattern that promotes the separation of an application into three main components: Model, View, and Controller.
Model: The model is responsible for managing the application's data, including data validation, storage, and retrieval from the database. It represents the business logic of the application.
View: The view is responsible for presenting the data to the user. It generates the HTML output and handles user interface components. The view is kept as minimal as possible, focusing on the presentation aspect.
Controller: The controller acts as an intermediary between the model and the view. It receives user input, processes it, interacts with the model to fetch or modify data, and then passes the relevant data to the view for display.
The MVC pattern enhances code organization, making it easier to maintain, extend, and collaborate on projects.
3. Routing:
Routing is a critical aspect of PHP application architecture, especially for web applications that have multiple pages and user interactions. Routing involves mapping URLs to specific controller actions or methods. By defining routes, you can establish clean and user-friendly URLs that correspond to different parts of your application. Popular PHP frameworks like Laravel, Symfony, and Slim offer robust routing mechanisms that simplify the process of handling incoming requests and directing them to the appropriate controllers.
4. Dependency Injection:
Dependency injection is a design pattern that improves code modularity and testability by allowing components to be loosely coupled. Instead of creating dependencies within a class, you inject them from outside. This makes it easier to replace components, mock dependencies for testing, and maintain a more flexible architecture.
5. Database Interaction:
PHP applications often require interaction with databases to store and retrieve data. When architecting the database layer, it's crucial to consider factors such as data integrity, performance, and security. Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) libraries like Doctrine provide tools to manage database interactions while abstracting away the complexities of raw SQL queries.
6. Scalability and Performance:
As your PHP application grows, ensuring scalability and performance becomes essential. Utilize caching mechanisms, optimize database queries, and consider using content delivery networks (CDNs) for serving static assets. Horizontal and vertical scaling strategies should also be considered based on the application's needs.
Conclusion:
Mastering the fundamentals of PHP application architecture empowers developers to build maintainable, scalable, and efficient web applications. By adhering to principles such as separation of concerns, MVC, routing, dependency injection, and efficient database interactions, you can create codebases that are easier to maintain, extend, and collaborate on. Whether you're working on a small project or a large-scale application, these architectural concepts will guide you towards creating successful PHP applications.
0 notes
Text
Explain the concept of route model binding in Laravel

Introduction:
Laravel Web Development Company in india, an acclaimed PHP framework, has gained immense popularity for its elegant syntax, extensive features, and developer-friendly approach. Among the many powerful functionalities it offers, "Route Model Binding" stands out as an efficient way to simplify data retrieval and manipulation in Laravel web applications. This concept allows developers to seamlessly connect URL parameters to corresponding model instances, enhancing code readability, and promoting cleaner, more maintainable code. In this blog, we will delve into the concept of Route Model Binding in Laravel, exploring how it streamlines the development process and benefits businesses leveraging Laravel Development Company India.
What is Route Model Binding?
Route Model Binding is a technique in Laravel that automatically injects model instances directly into controller methods based on the URI segments. Instead of manually fetching data from the database using route parameters, developers can define route parameters that correspond to model IDs, and Laravel automatically fetches the appropriate model instance from the database and injects it into the controller method. This elegant approach simplifies data retrieval and eliminates the need for repetitive database queries, making code more concise and maintainable.

Defining Route Model Binding:
In Laravel, setting up Route Model Binding is straightforward. Developers need to define the binding in the RouteServiceProvider or within the RouteServiceProvider's boot method. For example, if a route parameter {user} corresponds to the User model, the binding can be defined as follows:
Implicit vs. Explicit Route Model Binding:
Laravel offers two types of Route Model Binding: Implicit and Explicit.
a. Implicit Route Model Binding:
With Implicit Route Model Binding, Laravel assumes that the route parameter's name matches the name of the associated model's variable in the controller method. For instance, if the route parameter is {user}, Laravel will automatically bind it to a variable named $user in the controller method.
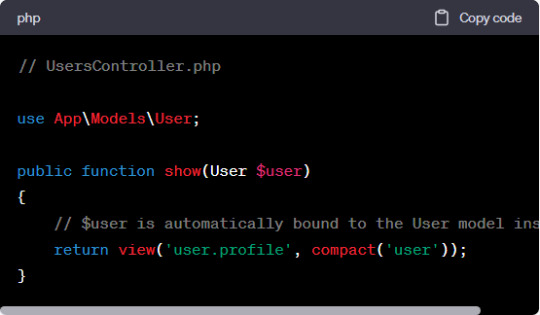
b. Explicit Route Model Binding:
Explicit Route Model Binding allows developers to specify custom binding logic for route parameters that do not match the model's variable name in the controller method. This method gives developers more control and flexibility over how models are retrieved.

Benefits of Route Model Binding:
The advantages of leveraging Route Model Binding in Laravel Development Company are significant:
a. Simplified Data Retrieval:
Route Model Binding automates the process of fetching model instances based on route parameters, reducing the need for manual database queries. This simplifies data retrieval, making code more expressive and concise.
b. Improved Code Readability:
By using Route Model Binding, developers can directly access the model instances within the controller methods using the associated variable names. This enhances code readability and makes it easier to understand the data being manipulated.
c. Reduced Database Queries:
Route Model Binding eliminates the need for multiple database queries to fetch data, reducing the load on the database and improving the application's overall performance.
d. Easier Error Handling:
With Route Model Binding, developers can effortlessly handle situations where the requested model instance does not exist. Laravel automatically returns a 404 Not Found response, simplifying error handling and enhancing the user experience.
Conclusion:
Route Model Binding is a powerful feature offered by Laravel, streamlining the process of data retrieval and manipulation in web applications. By automatically injecting model instances into controller methods based on route parameters, developers can significantly simplify code, improve readability, and reduce database queries. Businesses seeking Laravel Development Agency India can benefit from this elegant technique, ensuring the development of efficient, maintainable, and high-performing web applications. With the help of skilled Laravel developers and the application of Route Model Binding, businesses can unleash the full potential of their Laravel-powered web projects, driving success and growth in the competitive digital landscape.
#LaravelDevelopmentCompanyIndia#LaravelDevelopmentAgencyIndia#LaravelWebDevelopmentCompanyinindia#DigitalMarketingCompanyIndia#DigitalMarketingAgencyIndia#TopSEOAgencyIndia#SEOCompanyIndia#ShopifyDevelopmentCompanyIndia#MagentoDevelopmentCompanyIndia
0 notes
Text
Laravel camelcase json Response
You all know that the naming convention for database fields should be in the snake_case format. Hence, fetching the data from the database will also result in the snake_case format.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
How to Plan for Your Big Mobile App Launch?

Have you ever thought what number of users may hit your mobile app once it goes public? As soon as the mobile app launches to the App Store or Play Store, it's available for the general public to download and begin using. But is your app capable of managing a sudden influx of installations and traffic? Any mobile app must be developed in a way so that it can manage high traffic for your big mobile app launch.
A mobile app usually contains the subsequent factors:
Mobile App Development
The mobile app is often developed using Native or Hybrid technology. Each technology has pros and cons.
Web Admin Panel Development
The Web admin panel allows the admin users or managers to work out the activities of users who are using the mobile app.
The admin panel is specially developed employing web technology (PHP, Laravel, etc.) and shows all the activities recorded from the app.
Web Services
Web services are called middle layers and are accustomed to communicate the information flow between the mobile app and also the web admin together with a database.
All dynamic content is updated or fetched from the database using web services.
When we speak about managing a large user base, all the factors mentioned above must be developed in an exceedingly way so performance doesn't fall when hundreds or thousands of users hit the app.
The subsequent points must be reviewed and managed while developing a mobile app to manage heavy traffic:
Backend Server (Hosting server)
Improving the performance of the app depends on the performance of the server that hosts your database and Web Services (APIs). The server needs to be capable of managing the traffic easily. It needs to contain the hardware and the applications that are installed on the server.
Database Transactions
A well-structured database helps with:
Saving space by removal of redundant data
Providing data access faster
Keeping data accuracy and integrity
The other important part is how we manage transactions with the database. Can we write queries that are slow to retrieve data? Can we create multiple joins while retrieving data from the database? Your query writing skills can completely change the performance of your app.
It’s important to put in writing queries that help:
Specify the sphere name from which to urge data (Don’t use select * from a table after you need access to only some columns)
Use short queries rather than multiple joins (Multiple joins within the queries can take a protracted time to fetch data)
Search on the indexed columns
Long processes in Background tasks
From a user engagement point of view, it’s always good to place long-running tasks within the background thread, so that the UI thread doesn’t get blocked. it'll help app users continue acting on their app activities without anticipating data to be processed on the forepart.
Make fewer calls to APIs
Making lots of API calls takes up lots of the method within the background. If there are fewer calls to the APIs it'll help run the mobile app effectively. APIs communicate with the database using the queries mentioned above. So each call to an API will get a knowledge result set. looking at the scale of knowledge, and therefore the time taken by the queries, this might slow the app response. So until there's a desire, don't make calls to APIs.
Contact Treevibes Technologies iOS Mobile App Company in Chennai to induce started on your big mobile app launch.
Optimized code
Code quality also plays a key role in app performance. There are several points one should keep in mind while writing code.
Avoid Creating Unnecessary Objects: Unnecessary objects cause the rubbish collector to be called unnecessarily, which successively eats resources needed to spice up the performance of the application.
Avoid Background Services: Background services should be avoided to stay running unless required, as they keep occupying the resources throughout their execution.
Use Standard Libraries: rather than implementing the identical functionality in your code, use the already available resource.
Use Optimized Data Containers’
Use Cache: Objects which are expensive to form should be implemented in the cache. For instance, if you've got to display some images from the web, then you ought to hold them in memory to avoid downloading them several times.
Conclusion
Treevibes Technologies Android App Development Company in Chennai is created by experienced app developers. We use Native and Hybrid technologies for developing mobile apps. As for that app we launched, after the launch, our client was thrilled because he heard little or no from users. No news is nice news after you do a giant mobile app launch. The app worked of course and therefore the next phase will begin soon.
Contact Treevibes Technologies Mobile App Development Company in Chennai to induce started on your big mobile app launch.
We create complex web and mobile applications. We assemble expert Indian developers – ranked among the highest in their field – and India-based, American relationship managers, who provide stateside context for clients’ needs and expectations. This mix creates a replacement reasonably contracted development that doesn’t trade quality for cost.
#mobile app development company in chennai#android app development company in chennai#mobile development company in chennai#ios app development company in chennai#ios mobile app company in chennai#mobile application development in chennai#flutter mobile app development company in chennai#leading mobile application developers in chennai#e-commerce app development company in chennai#best mobile app company in chennai#game development company in chennai#treevibes technologies
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Laravel 5.8 Tutorial From Scratch - e26 - Vue Basics 101 - Laravel
Laravel 5.8 Tutorial From Scratch – e26 – Vue Basics 101 – Laravel
Laravel 5.8 Tutorial From Scratch – e26 – Vue Basics 101 – Laravel
[ad_1]
Vue is a modern Javascript framework that is powerful but yet simple to understand. In this episode, we are covering the basics of Vue by setting up a reusable button component. We will wrap it up by fetching some data from the Laravel backend using Axios.
For the best experience, follow along in our interactive school at h…
View On WordPress
#fetching data in laravel#full stack vue#laravel#laravel 5.8#Laravel API#laravel axios post example#laravel fetching data from database#laravel front end#laravel frontend tutorial#laravel mix#laravel mix 5.8#laravel mix vue#laravel node modules#laravel npm install#laravel vue#laravel vue js crud#laravel vue setup#laravel vue tutorial#laravel vue.js#laravel webpack tutorial#npm run dev#npm run watch laravel#vue#Vue.js#vuejs laravel
0 notes